The dependency graph
Designers of electronic systems produce thousands of files with help of their computer tools. The files depend on each other in complex ways. If a designer changes a file, that change must eventually propagate to all dependent files. If the propagation is incorrect, the design will be inconsistent and the consequences will be costly.VOV uses a technique called run-time tracing, which is based on the observation that only the tool knows accurately the dependencies implied by its use. VOV offers two ways for tools to communicate the dependency information at run-time:
- Encapsulation
- consists normally of a shell script that computes the run-time dependencies, communicates them to the dependency manager, and then calls the tool. It is a powerful technique that does not require any modification of the tool. For the many tools that have already been encapsulated, the encapsulation effort has gone from a few minutes to a few weeks of work, depending on the complexity of the tool.
- Integration
- is an option for those who have access to the
source code of the tool; it is faster and easier than encapsulation.
The VOV Integration Library (VIL) consists of 600 lines of
C code distributed in source format.
The integration library is passive if VOV is not running; the integrated tool behaves exactly as the original tool.
Architecture
The client/server architecture of VOV supports concurrent activities, team coordination, distributed data management, and distributed processing.
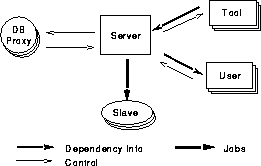
The server is the UNIX process that manages the design trace. Depending on the operating system, the server can handle up to 250 clients simultaneously. There are four classes of clients:
- Tools
- connect to the server to declare their inputs and outputs, thus allowing the server to build the design trace.
- Users
- connect to the server to query and possibly modify the trace. There are four user interfaces avaliable.
- Slaves
- offer computing resources to the server. Whenever the
server decides that some tool needs to be executed, it will
search the list of slaves for the best one that can do the job.
The slaves are processes running on the various machines in the local area network. They are an integral part of the network computing subsystem in VOV.
- Proxies
- contribute knowledge about databases.
The server does not know anything about databases. All the knowledge is provided externally by means of these proxies. This allows VOV to work with any databases, not just with UNIX files.
Since UNIX is always needed, support for UNIX has been moved back into the server.
Archiving methodologies
Useful and proven design methodologies can be archived and retrieved for reuse. The VOV assistant guides you through the library of existing methodologies and extracts data and flow information from them.
Your makefiles and scripts can be useful to build the
design trace. VOV can convert the trace
into a makefile or a shell script.
Many tools are already encapsulated
Runtime Design Automation provides capsules for selected tools from Cadence, Exemplar Logic, interHDL, Model Technology, Synopsys, ViewLogic, and Xilinx, as well as for many UNIX utilities and C and C++ compilers.Platforms
VOV is available on AIX, DEC-Alpha, HAL HP-UX, Linux, SunOS-4.x, Solaris-2.Back to index
© Copyright 1996 Runtime Design Automation